ShelfAware - Real-Time Semantic Localization in Quasi-Static Environments
2024-2025 - In submission
Team members:
Shivendra Agrawal, Jake Brawer, Ashutosh Naik, Alessandro Roncone, Bradley Hayes
2025
Abstract
Localization in dynamic, visually aliased environments like grocery stores is a difficult challenge for autonomous systems. Aisles often look identical geometrically, and stock changes frequently. ShelfAware is a novel semantic localization framework that achieves robust, real-time global localization using only low-cost sensors—specifically, a monocular RGB-D camera on a smartphone. Unlike traditional methods that rely on expensive LiDAR or detailed geometric maps, ShelfAware uses a Semantic Particle Filter. It leverages Visual-Inertial Odometry (VIO) for motion estimation and corrects drift by matching detected product categories (e.g., “cereal”, “soda”) against a lightweight semantic map. This allows the system to localize accurately even in featureless or repetitive aisles.

The ShelfAware Approach
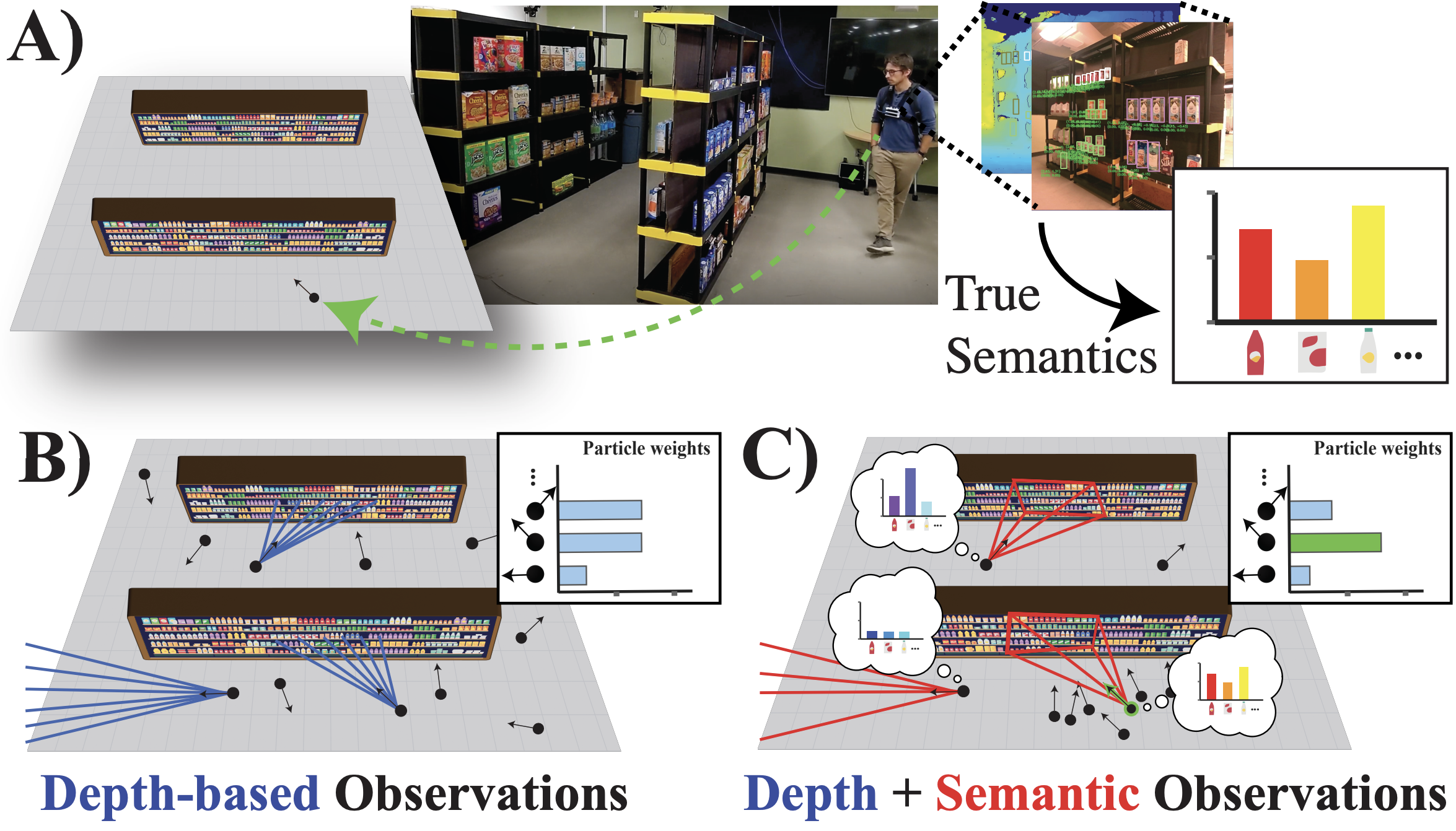
The core of our solution is a particle filter that fuses visual-inertial odometry with semantic observations.
- Semantic Mapping: We utilize a pre-built semantic map that stores the locations of product categories rather than individual items, making the map robust to daily stock changes.
- Observation Model: As the agent moves, a custom YOLO-based detector identifies product categories in the camera frame.
- Particle Update: We project these detections into 3D space. Particles that “expect” to see the detected products at their hypothesized location receive higher weights, while those that don’t are penalized. This effectively converges the particle cloud to the robot’s true location.
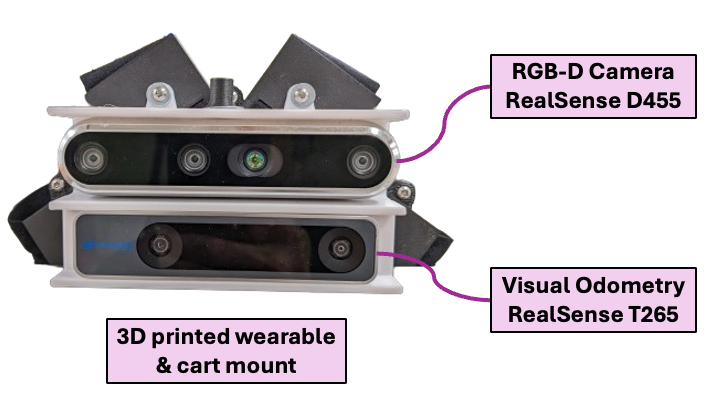
Modularity
- Mountable on Carts/Strollers: Can add autonomous capabilities to existing equipment.
- Wearable: Can support assistive technology for navigation.


Algorithm
-
Semantic Mapping
We trained a custom classifier to classify products into a fixed number of classes.

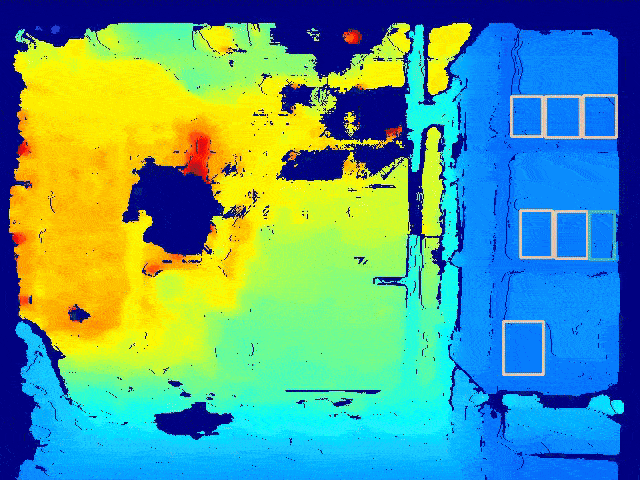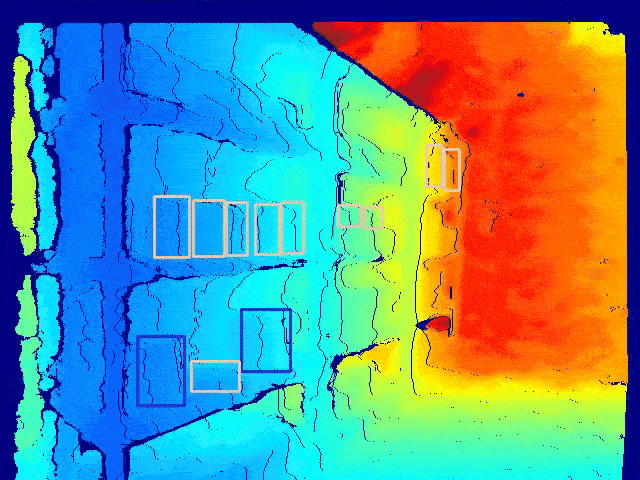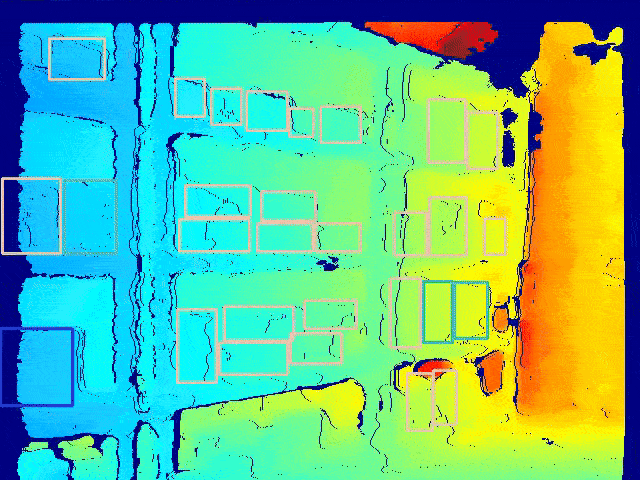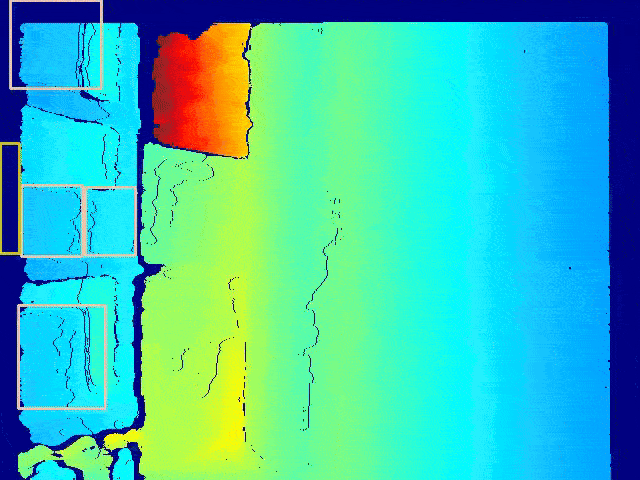
-
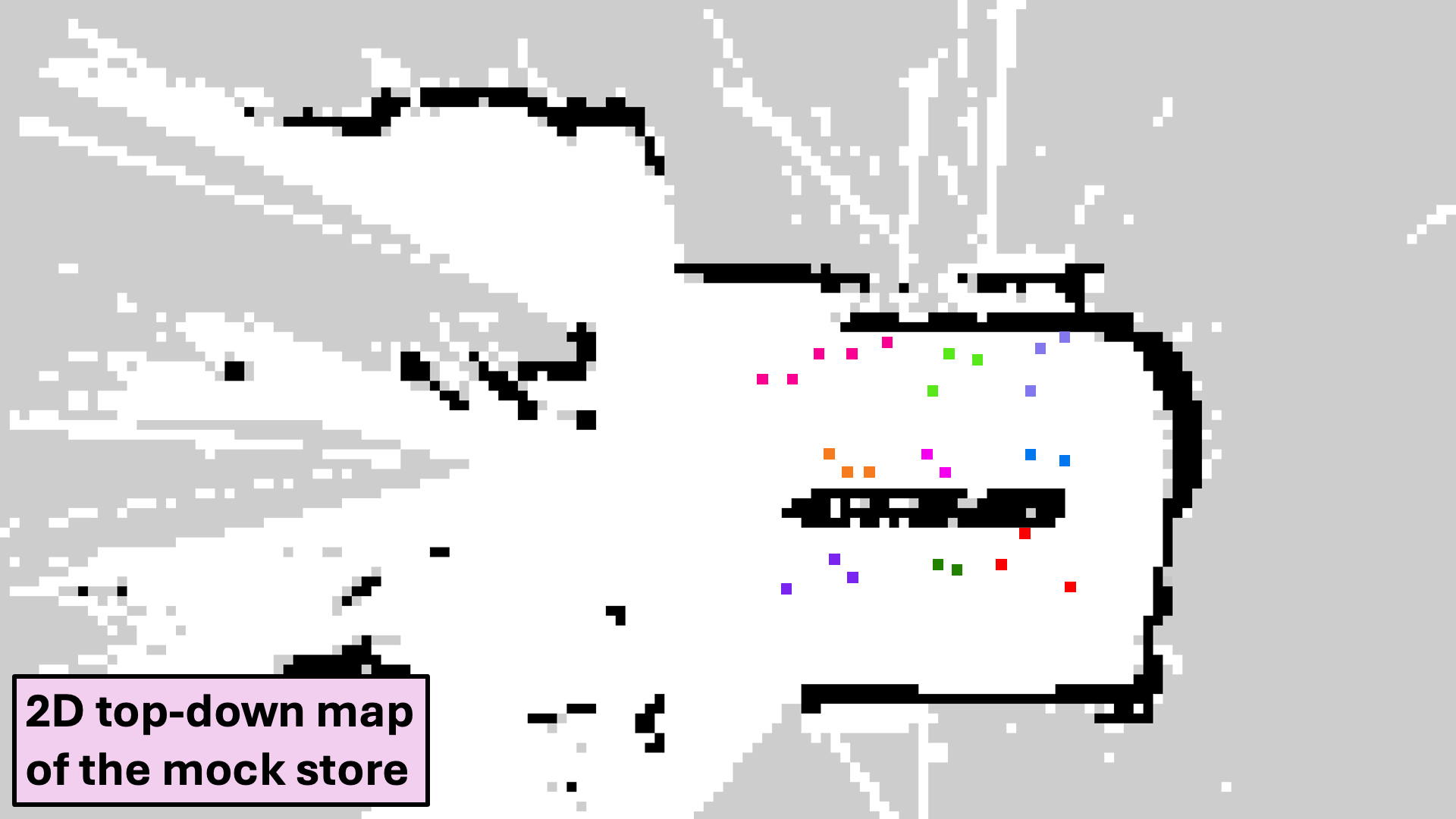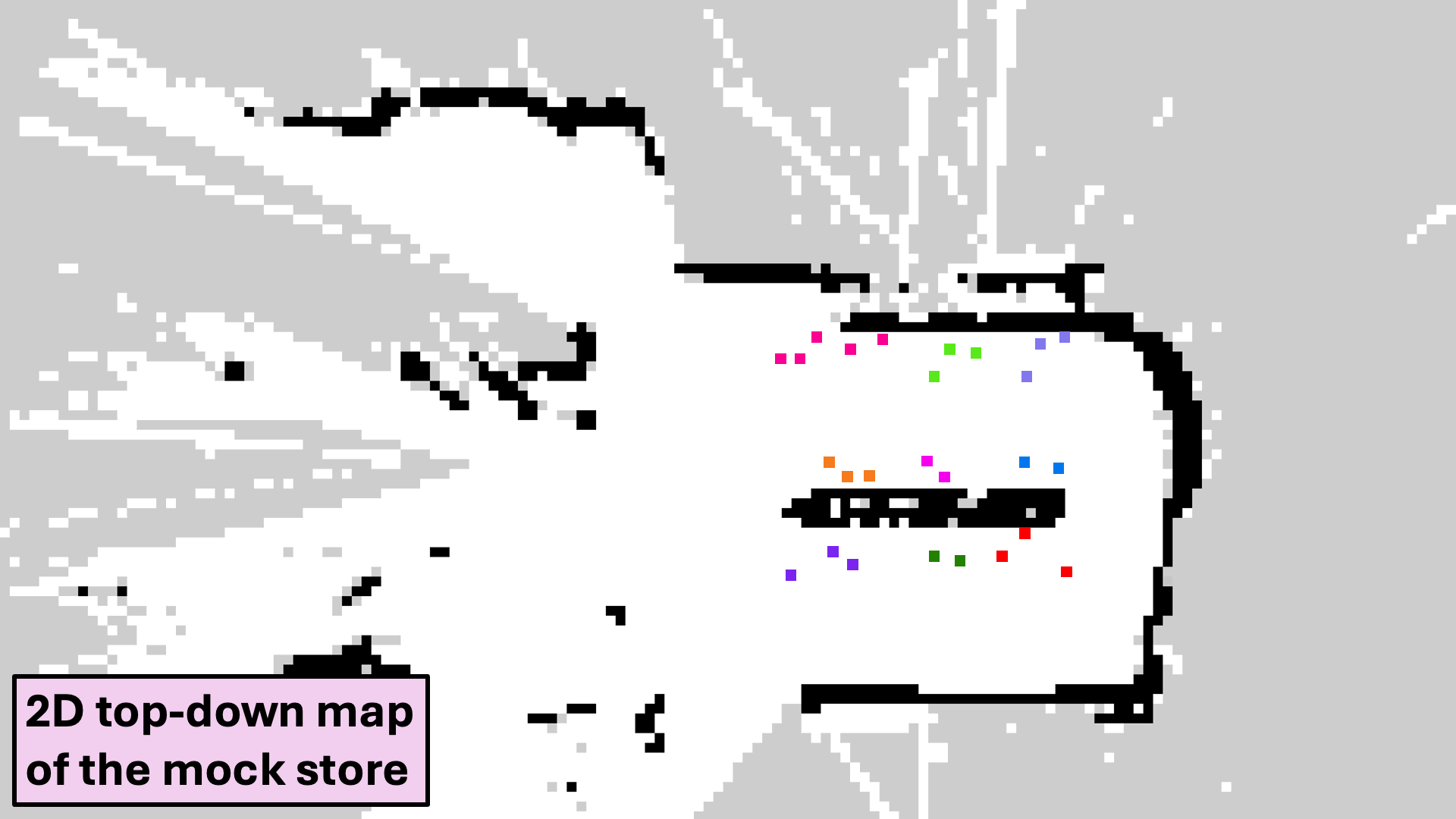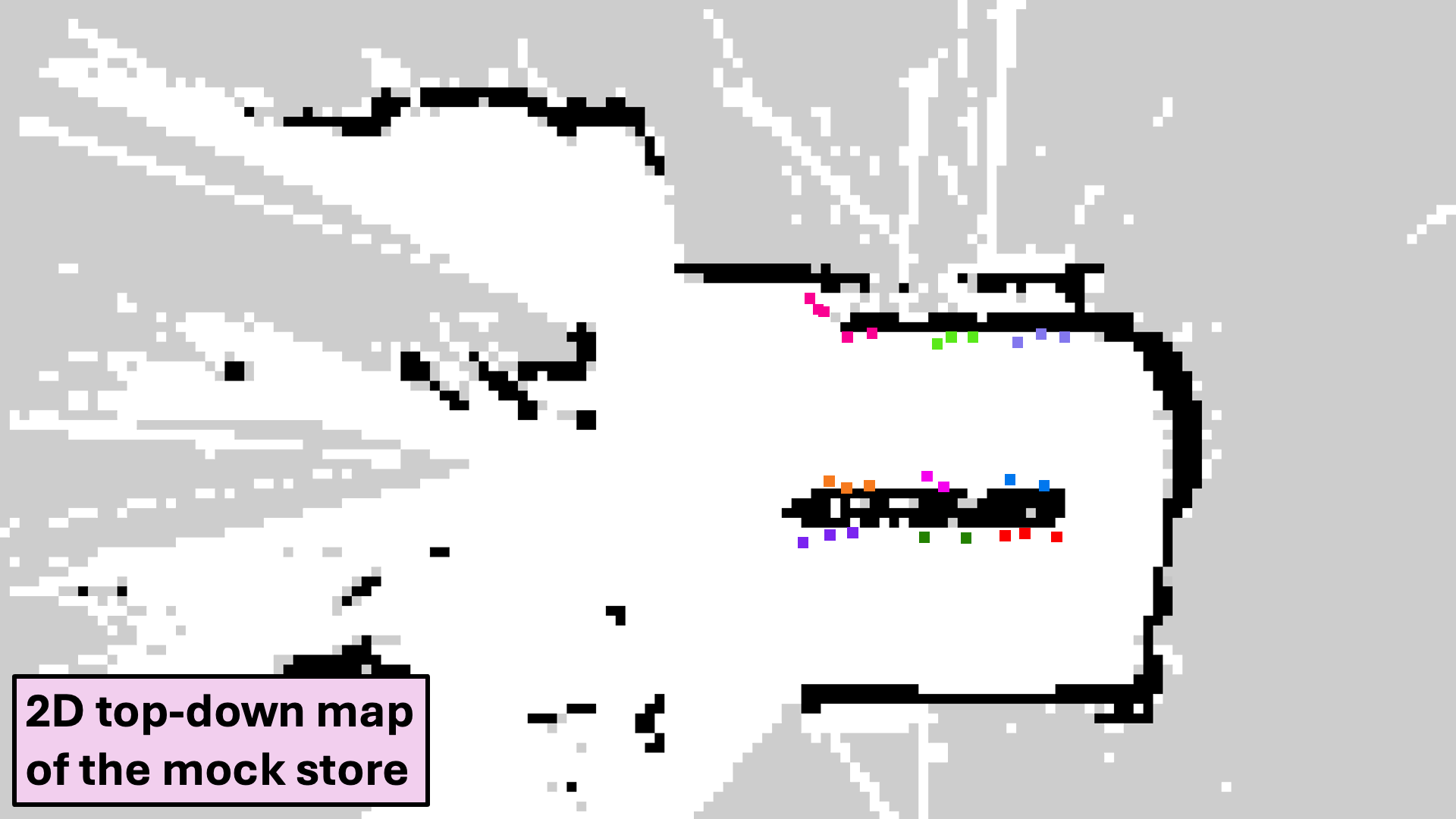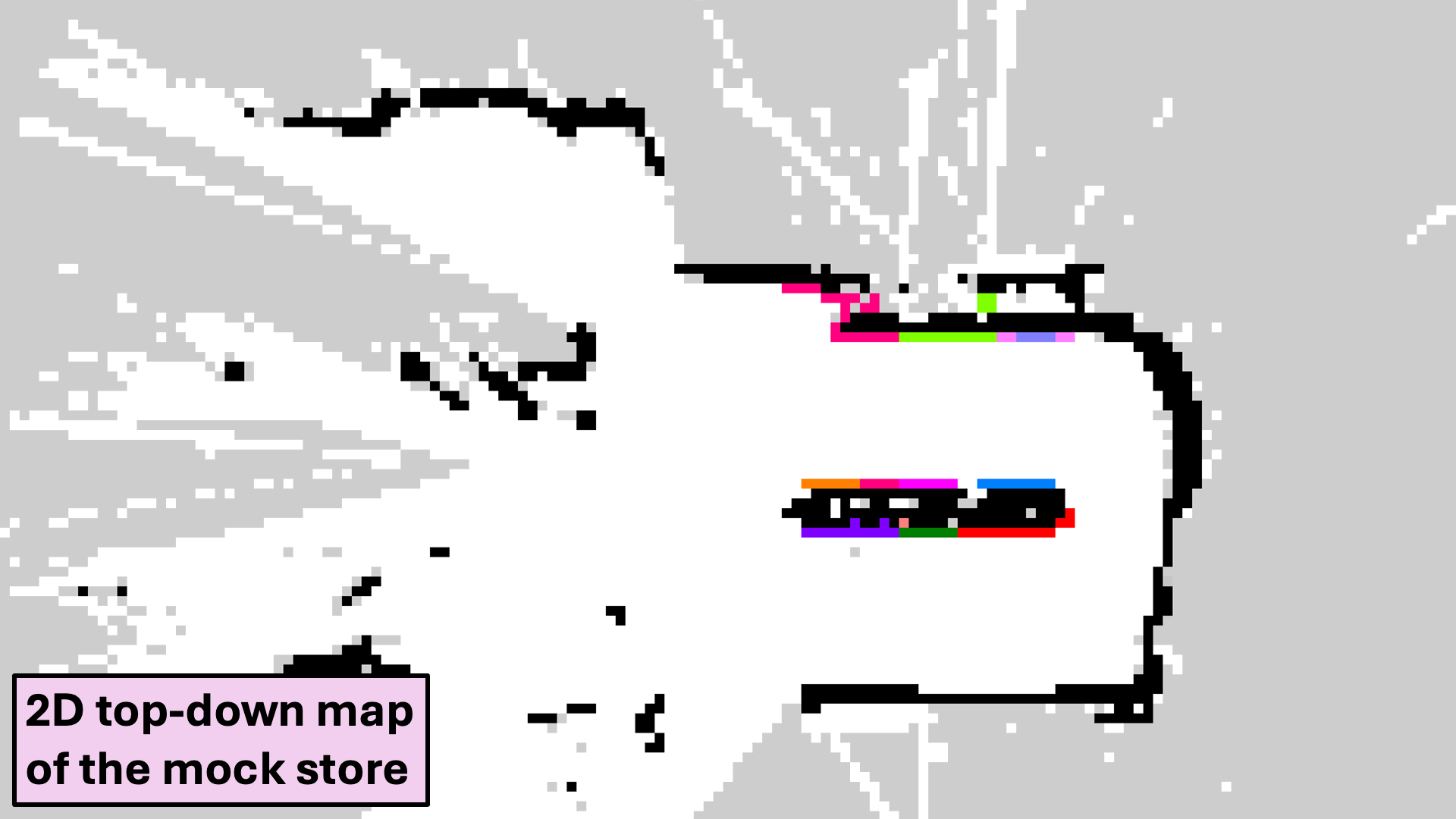
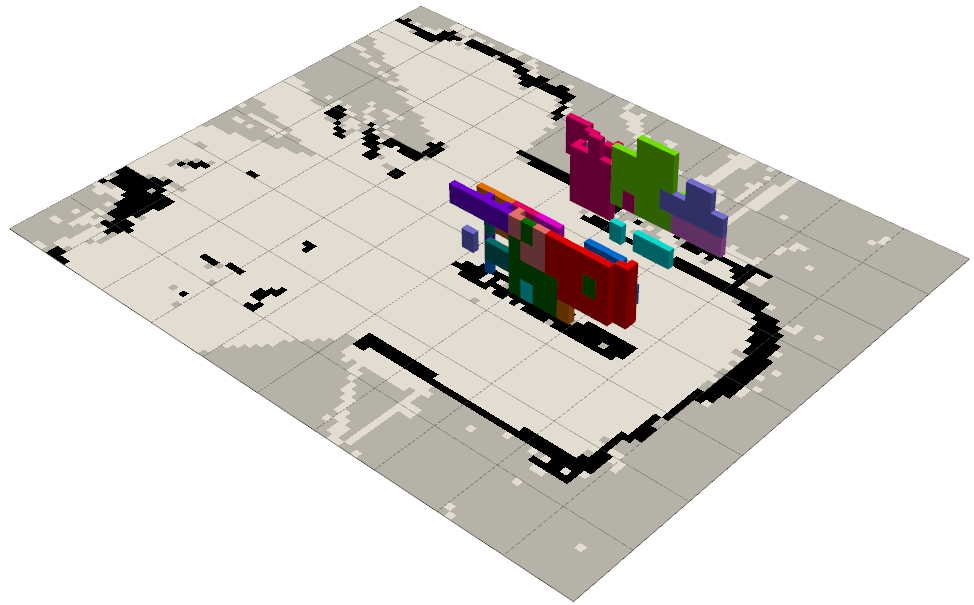
Pose Correction
Real-world pose estimates obtained through inverse camera projection are refined using ray casting on the semantic map.
-
Semantic Localization
Semantic information is fused with the depth observation to in a Monte Carlo Localization framework.
Demo
Experimental Results
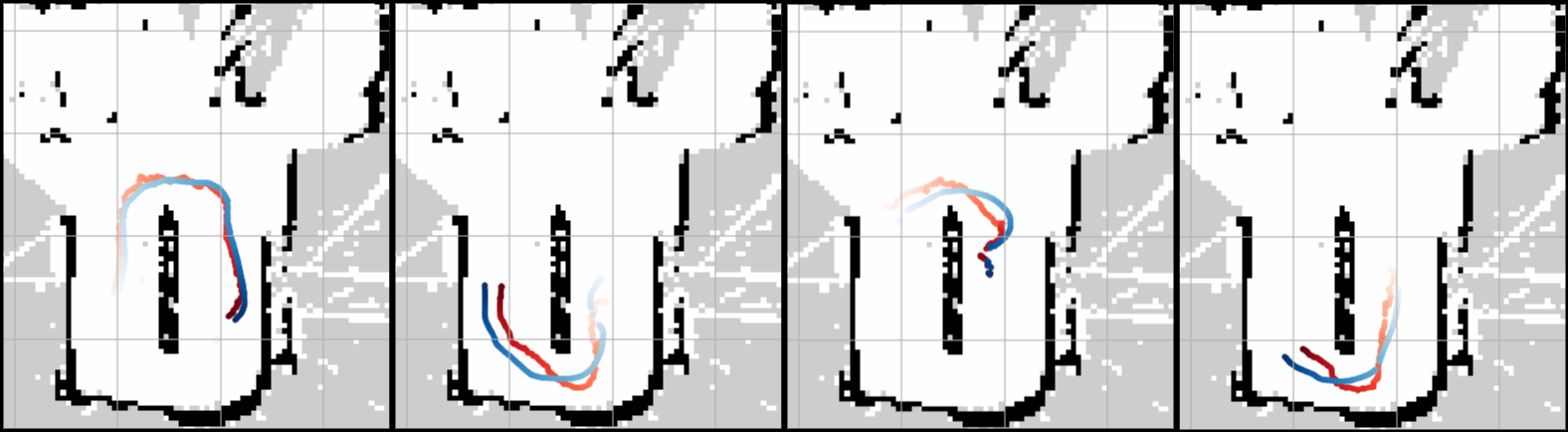
We evaluated ShelfAware in a semantically dense retail environment (a mock store) across diverse conditions, including cart-mounted and wearable setups. The system achieved a 96% global localization success rate with a mean time-to-convergence of 1.91s, significantly outperforming geometric baselines like MCL (22% success) and AMCL (10% success). The system operates in real-time (9.6Hz) on consumer laptop-class hardware, demonstrating robust tracking even in dynamic, visually aliased aisles.
@article{agrawal2025shelfaware,
title={ShelfAware: Real-Time Visual-Inertial Semantic Localization in Quasi-Static Environments with Low-Cost Sensors},
author={Agrawal, Shivendra and Brawer, Jake and Naik, Ashutosh and Roncone, Alessandro and Hayes, Bradley},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2512.09065},
year={2025}
}